A chart of accounts (COA) is a financial organizational tool that provides a complete listing of every account in an accounting system. An account is a unique record for each type of asset, liability, equity, revenue, and expense.
The chart of accounts (COA), which lists the names of the accounts that a company has identified and made available for recording transactions in its general ledger. Typically, a COA contains the account’s names, brief descriptions and identification codes.
In practice, the COA serves as the foundation for a company’s financial record-keeping system. It provides a logical structure that facilitates the addition of new accounts and the deletion of old accounts.
Within the COA, accounts will be typically listed in order of their appearance in the financial statements. Typically balance sheet accounts are listed first followed by the income statement accounts.
| Balance Sheet Accounts | Assets |
| Liabilities | |
| The owner (stockholders) ‘s equity | |
| Income statement accounts | Operating Revenues |
| Operating Expenses | |
| Non-Operating Revenues and Gains | |
| Non-Operating Expenses and Losses |
An important purpose of COA is to segregate expenditures, revenue, asset, and liabilities so that the viewers can quickly get a sense of a company’s financial health.
In SAP, the Chart of Accounts (COA) is defined at the client level and assigned to each company code. It is a list of General Ledger account’s master data that fall under different account groups of a company code. This grouping mechanism helps to develop better financial reports.
Types of Chart of Accounts
There are three types of Chart of Accounts, viz
- Operating chart of accounts: They are used to post daily expenses. The accounts in the Operating Chart of Accounts could be either expense or revenue accounts, and the information is shared by Finance as well as Controlling modules.
- Group Chart of Accounts: These are accounts used by the entire corporate group. They help in generating reports at the corporate
- Country-specific chart of accounts: This Chart Of Accounts help meet country-specific legal requirements
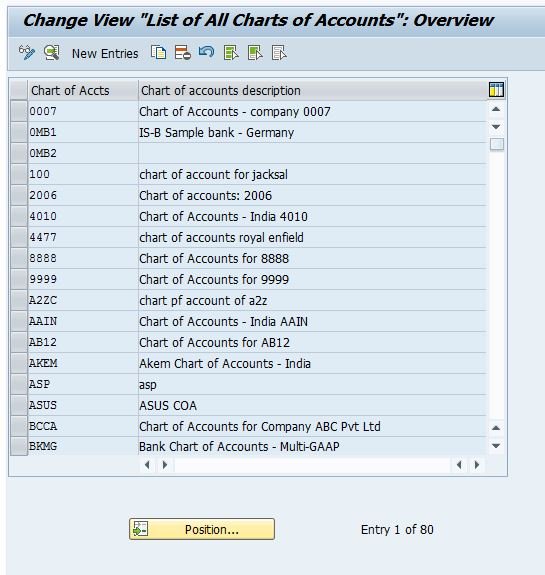
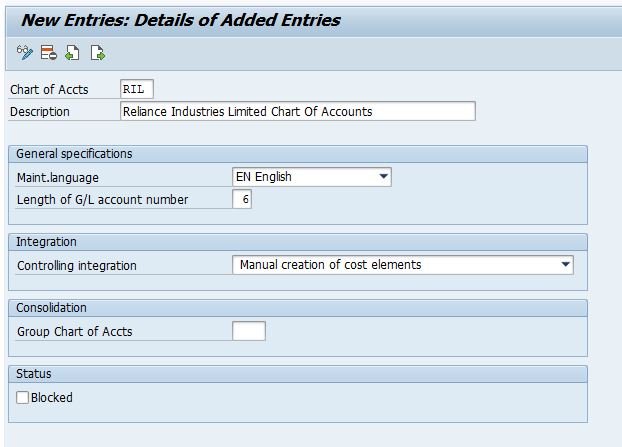
Path: IMG -> Financial Accounting -> General Ledger Accounting -> G/L Accounts -> Master Records -> Preparations -> Edit Chart of Accounts List
TC:- OB13
| Field Name | Description |
| Chart of Accts | Unique alphanumeric code for identifying the Chart Of Accounts. The maximum allowable length is four digits. |
| Description | Description for the Chart Of Accounts |
| Maint.language | Language in which the chart of accounts is created. All accounts have a description in this language. Master Data can only be displayed or maintained in this language. |
| Length of G/L account number | The maximum length for G/L Accounts Number, it could be maximum to ten (10) digits if the number is short then it will be prefixed zero before it to make it to the maximum length. |
| Controlling integration | We can have controlling integration a) Manual creation of cost elements b) Automatic creation of cost elements it is preferable to have manual creation of cost elements in SAP financial accounting. We have to keep in mind that whenever we create a GL code (expense or revenue account) in Financial Accounting, at the same time we have to create the cost element (type 1 or 11) in the controlling module of the SAP system. This allows cost to be flown from FI to CO on a cost object in Realtime |
| Group Chart of Accts | If we have more than one company code and all company codes are using different operating chat of Accounts(COA) then cross-company code controlling will not be possible by using the controlling area. To avoid this problem one can use group COA. A group COA is used for consolidation purposes when more than one operational COA is used by different codes. Group COA is helpful for internal reporting. |
| Blocked | When we tick the blocked it will disable the COA |







